Developmental Stages of Multi-Generational Family Businesses
A few weeks ago I had the pleasure of hearing Lena Jungell, a fourth-generation member of The Fazer Group, speak at the Fall 2015, Global Family Business Event hosted by the Baruch College, Lawrence N. Field Center for Entrepreneurship.
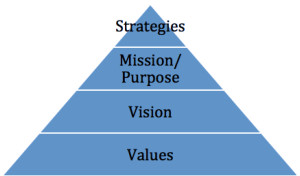
In her talk, Ms. Jungell presented elements essential for the growth and sustainability of a multi-generational family business. In my last two newsletters I touched on three of these: Vision, Values and Mission.
Ms. Jungell presented a fourth critical element–outlining the developmental stages of her family and its business across generations:
- First generation: Built the business
- Second Generation: Lived with and worked in the business
- Third Generation: Worked in the business and established business-governance structures
- Fourth Generation: Developed family-governance structures
- Fifth Generation: Learned the business- and family-governance structures
- Sixth Generation: Is already participating in the business while the fifth generation governs.
This pattern is fairly typical of family-business succession. I believe it is representative of a business that successfully evolves into a multi-generational enterprise without an initial intention to do so. Recognizing the pattern can facilitate the growth of any business family interested in multi-generational success.